V2649. MISRA. All arguments of any type-generic macros from <tgmath.h> should have an appropriate essential type.
This diagnostic rule is based on the MISRA (Motor Industry Software Reliability Association) software development guidelines.
This diagnostic rule is relevant only for C.
All arguments passed to macros from the <tgmath.h> header file must have one of the following types: essentially signed, essentially unsigned, essentially real floating, essentially complex floating.
These types are intended for arithmetic operations. From here on, we will refer to them as arithmetic types.
The MISRA standard defines its own type model (Essential type model).
Using the essentially complex floating type arguments for the following macros may lead to undefined behavior:
atan2, cbrt, ceil, copysign, erf, erfc, exp2, expm1, fdim, floor, fma, fmax, fmin, fmod, frexp, hypot, ilogb, ldexp, lgamma, llrint, llround, log10, log1p, log2, logb, lrint, lround, nearbyint, nextafter, nexttoward, remainder, remquo, rint, round, scalbn, scalbln, tgamma, trunc
Note. The last argument of the frexp and remquo macros is for output, and its type may differ from the others.
Using non-arithmetic types as arguments can lead to undefined behavior, since they cannot be converted to the real types used in macros from the <tgmath.h> header file.
The example:
#include <tgmath.h>
char sampleSqrt(char ch)
{
return sqrt(ch);
}Here, a variable of the char type is used as an argument for the sqrt macro. Expanding the macro results in a call to a function that takes the double type argument, which is then converted to the double type. However, according to the MISRA standard, char is not an arithmetic type and should not be used for calculations.
Converting between numeric and character types is meaningless because these two representations do not correspond. As a result, such a conversion may lead to undefined behavior. The MISRA standard provides a table of type conversions and cases where such conversions should be avoided:
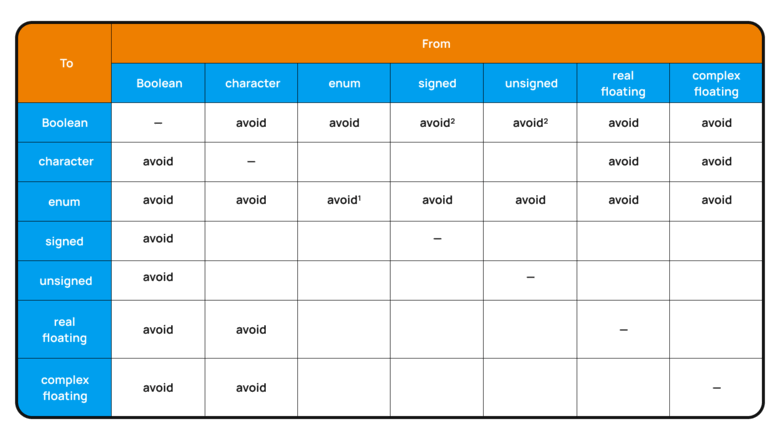
The exceptions:
- A variable of the
enumtype can be converted to a synonym of the same type. - Variables with constant values of
0and1can be converted from an integer type toBoolean.
In this case, it is worth using one of the real types, for example, double.
The fixed code:
#include <tgmath.h>
double sampleSqrt(double ch)
{
return sqrt(ch);
}This diagnostic is classified as:
|
