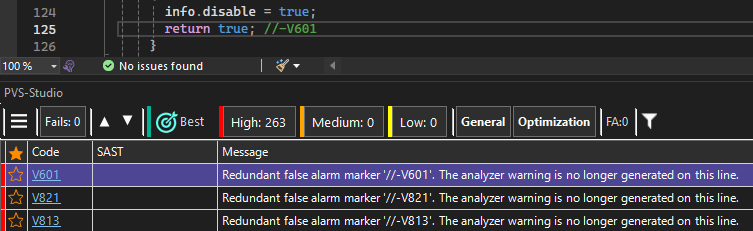
How to delete redundant false alarm markers
- False alarm markers for deletion
- How to collect information about redundant markers
- How to automatically delete redundant markers
- How to merge reports on redundant false alarm markers
- How to create a report for preview
As the analyzer evolves or the analyzed code changes, a warning on false positive may stop appearing, and false alarm markers left in the source code for that warning become redundant.
When such redundant markers accumulate, they clutter the code and can cause a new warning to go unnoticed when it appears in the same spot.
To clean the codebase of redundant false alarm markers, PVS-Studio distribution includes a dedicated utility: pvs-fp-cleaner.
False alarm markers for deletion
To suppress false-positive warnings, PVS-Studio analyzer supports control comments of the following type:
//-Vwarning-number
The warning-number is the diagnostic rule number.
Examples of false alarm markers:
if (a == b && a == b && 0 / 0 == 0) //-V501 //-V609If you suppress a false positive using the hash code mechanism, the tool also considers the following markers for removal:
//-VH"hash"
The hash is the hash code of a line excluding comments.
Here is an example of a marker with a hash code:
if (a == b && a == b && 0 / 0 == 0) //-V501 //-V609 //-VH"12345678"How to collect information about redundant markers
The first step in removing redundant false alarm markers is to thoroughly analyze the project in a special mode.
Currently, you can collect information only using the pvs-studio-analyzer / CompilerCommandsAnalyzer utilities.
The pvs-studio-analyzer / CompilerCommandsAnalyzer utility:
pvs-studio-analyzer analyze --redundant-false-alarms=/path/to/report.json \
--sourcetree-root=/path/to/project-root \
....As a result, a report on redundant false alarm markers will be created.
Required flags:
redundant-false-alarmsis the path to the created report on redundant false alarm markers;sourcetree-rootis the flag to specify the root directory (/path/to/project) of the project for building relative paths.
How to automatically delete redundant markers
To automatically delete redundant false alarm markers from the codebase, the distribution includes the pvs-fp-cleaner utility.
When you analyze code on different platforms, the analyzer may issue different warnings. So, for cross-platform projects, generate a separate report for each platform and pass all of these reports as input parameters to the cleanup utility.
After analyzing the project and receiving the report, you can run the cleanup utility by specifying the following arguments:
pvs-fp-cleaner cleanup \
--sourcetree-root=/path/to/project \
PATH...where
cleanupis the utility mode;PATH...is a list of paths to reports on redundant false alarm markers;sourcetree-rootis the path to the project root directory for converting relative paths from reports on different platforms.
The example:
pvs-fp-cleaner cleanup \
--sourcetree-root=/home/user/project \
/home/user/windows_report.json \
/home/user/linux_report.json \
/home/user/macOS_report.jsonWe recommend running the utility in the automatic cleanup mode on a codebase managed by a version control system such as Git, SVN, or Mercurial. If the project does not use version control, make sure to create a backup of the source files beforehand.
How to merge reports on redundant false alarm markers
If you need to merge several reports on redundant markers, for example, for a cross-platform project, you can also use the pvs-fp-cleaner utility.
pvs-fp-cleaner merge \
--sourcetree-root=/path/to/project \
--output-file=/path/to/merged_report.json \
PATH...where
mergeis the utility mode.sourcetree-rootis the path to the project root directory for converting relative paths from reports on different platforms. It is also used to merge information in identical files when analyzing them from different platforms.output-fileis the path to the resulting report after merging.PATH...is a list of paths to reports on redundant false alarm markers.
The example:
pvs-fp-cleaner merge \
--sourcetree-root=/home/user/project \
--output-file=/home/user/merged_report.json \
/home/user/windows_report.json \
/home/user/linux_report.json \
/home/user/macOS_report.jsonHow to create a report for preview
Before deleting false alarm markers, it may be useful to assess the scale of changes in the codebase. You can use the utility to create a report for previewing the detected redundant markers.
You can use the report mode to generate such a report:
pvs-fp-cleaner report \
--sourcetree-root=/home/user/project \
--output-file=/home/user/report_for_IDE_plugin.json \
PATH...where
reportis the utility mode.sourcetree-rootis the path to the project root directory for converting relative paths from reports on different platforms. In thereportmode, it is mandatory only when generating a report from "raw" core reports.output-fileis the path to the resulting report.PATH...is a list of paths to reports on redundant false alarm markers.
You can open the created report in your IDE using the provided plugins: