Webinar: Let's make a programming language. Part 1. Intro - 20.02
ReDoS is a type of a denial-of-service (DoS) attack. Its goal is to significantly slow down or halt program execution by exploiting a vulnerable regular expression.
The vulnerable regular expression takes a very long time to execute due to its construction peculiarities and the structure of the input string. In the worst case, the execution time of the regular expression can grow exponentially with the input size. Such scenarios are termed catastrophic backtracking—they cause slowdowns or complete halt of the program execution.
Catastrophic backtracking results from the operation of the backtracking function in the regex engine, which enumerates all possible string matches until it finds a correct one. If no valid match exists, the regular expression will continue to evaluate all possible combinations. Exhaustively processing a vast number of combinations leads to prohibitively long regex evaluations. This can cause significant freezes or even force a program to terminate. This is the essence of the ReDoS attack.
The following scenarios can enable ReDoS.
Regular expressions are vulnerable to catastrophic backtracking if they contain at least one subexpression that can generate a large number of matchings.
Look at a simple synthetic example for clarity.
Here is a regular expression:
(x+)+y
In which:
x+ matches one or more x characters;(x+)+ matches one or more repetitions of the x+ group;y matches the y character at the end of the string.Thus, the expression searches for a string where one or more "groups" consist of several x characters followed by the y character. For example, the xxy string fits this pattern.
Problems arise when a program processes the string that only partially matches the pattern, such as xxxx.
The issue occurs because the regular expression fails to find a match on the first attempt. So, the regex engine will test all possible combinations of "groups" containing one or more x characters. It continues until all possible options have been tried, as illustrated in the table below:
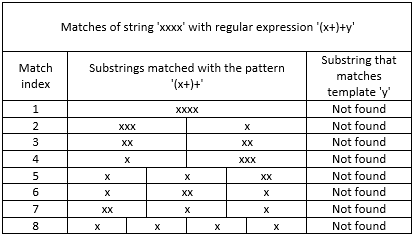
The more x characters the input string contains, the more combinations will be evaluated exponentially. Consequently, the regex execution time increases, leading to noticeable freezes and potential program crashes.
0